Jeff Bezos and Amazon: From Garage Bookstore to Global E-commerce Empire
Amazon, founded by Jeff Bezos in 1994, has grown from a humble online bookstore to a trillion-dollar eCommerce empire. This remarkable journey is a testament to strategic planning, innovative thinking, and a relentless focus on customer satisfaction.
This blog post will delve into the history of Amazon, highlighting the key strategies that have propelled the company to its current status as a global leader in eCommerce. Additionally, it will explore Jeff Bezos’s role in making Amazon successful and his professional attributes.
The Early Days of Amazon: A Garage Bookstore
Jeff Bezos, a former Wall Street executive, saw the potential of the internet in the early 1990s. Recognizing the untapped market for online retail, Jeff Bezos decided to start an online bookstore. He chose books because of their universal appeal and the vast number of titles available. In 1994, Bezos launched Amazon.com from his garage in Bellevue, Washington. The initial website was simple, offering a limited selection of books. However, Jeff Bezos’s vision was anything but modest. He aimed to create the “Earth’s biggest bookstore,” a goal that would eventually expand to encompass a wide range of products and services.

Jeff Bezos: The Visionary Leader
Jeff Bezos’s leadership has been instrumental in Amazon’s success. His visionary approach and long-term thinking have guided the company through various phases of growth. Bezos is known for his customer-centric philosophy, which prioritizes customer satisfaction above all else. This focus has driven many of Amazon’s innovative initiatives and has been a key factor in the company’s success.
Jeff Bezos is also known for his relentless pursuit of excellence. He sets high standards for himself and his team, constantly pushing the boundaries of what is possible. This drive for excellence has led to numerous innovations and improvements in Amazon’s operations and customer experience.
Expansion and Diversification
As Amazon gained traction, Bezos quickly realized the potential for expansion beyond books. In 1998, the company began to diversify its product offerings, adding music and videos to its inventory. This move was strategic, as it allowed Amazon to leverage its existing infrastructure and customer base to enter new markets. The diversification continued with the addition of electronics, toys, and other consumer goods. By the early 2000s, Amazon had transformed from a niche bookstore into a comprehensive online marketplace.
Revenue Growth
Amazon’s revenue growth has been impressive. In 1997, the company reported $147.8 million in revenue. By 2000, this figure had grown to $2.76 billion. The company’s revenue continued to climb, reaching $107.01 billion in 2015 and $280.52 billion in 2019. In 2020, Amazon’s revenue surpassed $386 billion, a testament to its dominant position in the eCommerce market.
According to Amazon’s latest financial reports, the company generated a revenue of ₹53.098 trillion (TTM). In 2023, Amazon’s revenue reached ₹47.850 trillion, marking an increase from the ₹42.532 trillion earned in 2022.
Customer-Centric Approach
One of the cornerstones of Amazon’s success is its unwavering commitment to customer satisfaction. Bezos has often emphasized the importance of putting the customer first. This philosophy is evident in several key initiatives:
- Prime Membership: Launched in 2005, Amazon Prime offers customers free two-day shipping on eligible items for an annual fee. This program has been instrumental in driving customer loyalty and increasing purchase frequency. As of 2021, Amazon Prime has over 200 million members worldwide, contributing significantly to the company’s revenue.
- Customer Reviews: Amazon was one of the first eCommerce platforms to allow customers to leave reviews for products. This transparency builds trust and helps customers make informed purchasing decisions.
- 24/7 Customer Service: Amazon’s customer service is available around the clock, ensuring that customers can get help whenever they need it. This level of support has been crucial in maintaining high customer satisfaction rates.
Technological Innovation
Amazon’s success is also attributable to its continuous investment in technological innovation. The company has developed several groundbreaking technologies that have enhanced its operational efficiency and customer experience:
- Amazon Web Services (AWS): Launched in 2006, AWS provides cloud computing services to businesses of all sizes. This division has become a significant revenue generator for Amazon, contributing to its overall growth. In 2020, AWS generated $45.37 billion in revenue, highlighting its importance to Amazon’s business.
- Kindle: Introduced in 2007, the Kindle e-reader revolutionized the way people read books. By offering a convenient and affordable way to access digital content, Amazon further solidified its position in the book market.
- Alexa and Echo: Amazon’s foray into voice-activated technology with Alexa and the Echo smart speaker has opened new avenues for customer interaction and engagement. These devices have become integral to many households, further integrating Amazon into daily life.
Logistics and Supply Chain Management
Efficient logistics and supply chain management are critical to Amazon’s success. The company has invested heavily in building a robust infrastructure to ensure timely delivery and optimal inventory management:
- Fulfillment Centers: Amazon operates numerous fulfillment centers worldwide, equipped with advanced automation technologies. These centers enable quick and accurate order processing, reducing delivery times and enhancing customer satisfaction.
- Drone Delivery: Amazon Prime Air, the company’s drone delivery service, aims to deliver packages to customers within 30 minutes of ordering. Although still in the testing phase, this initiative highlights Amazon’s commitment to pushing the boundaries of logistics.
- Third-Party Sellers: Amazon Marketplace allows third-party sellers to list their products on the platform, expanding the product range and providing customers with more options. This model has been highly successful, contributing significantly to Amazon’s revenue. In 2020, third-party sellers accounted for 55% of the units sold on Amazon.
Strategic Acquisitions
Amazon has also grown through strategic acquisitions, integrating complementary businesses to expand its offerings and market reach:
- Zappos: Acquired in 2009, Zappos is an online shoe and clothing retailer known for its exceptional customer service. This acquisition strengthened Amazon’s position in the fashion retail sector.
- Whole Foods Market: In 2017, Amazon acquired Whole Foods Market, a high-end supermarket chain. This move allowed Amazon to enter the grocery market, offering customers a seamless online and offline shopping experience.
- Ring: Acquired in 2018, Ring is a home security company that specializes in video doorbells and security cameras. This acquisition aligns with Amazon’s focus on smart home technology and enhances its product ecosystem.
Amazon’s most recent acquisition is MX Player, an ad-supported online video streaming platform founded in 2011 and based in Mumbai. Amazon acquired MX Player in October 2024.
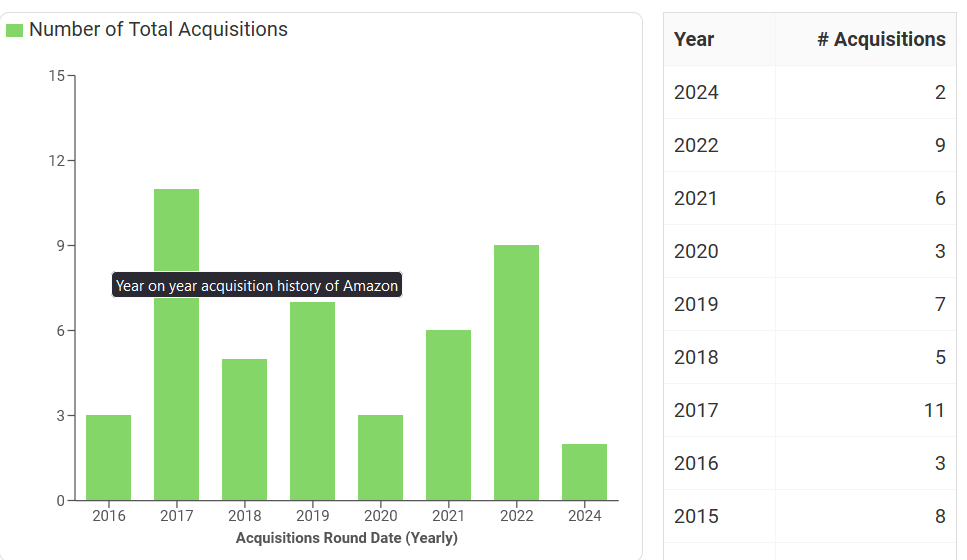
Global Expansion
Amazon’s growth has not been confined to the United States. The company has expanded its operations globally, establishing a presence in numerous countries:
- International Marketplaces: Amazon operates localized marketplaces in countries such as the United Kingdom, Germany, Japan, and India. These marketplaces cater to local preferences and regulations, ensuring a tailored shopping experience for customers worldwide.
- Cross-Border Trade: Amazon Global Selling enables sellers to reach customers in other countries, facilitating cross-border trade and expanding the company’s global footprint.
- Local Investments: Amazon has invested in local infrastructure, such as fulfillment centers and delivery networks, to support its global operations. These investments ensure efficient order processing and timely delivery, enhancing the customer experience.
Sustainability Initiatives
As Amazon has grown, it has also recognized the importance of sustainability. The company has implemented several initiatives to reduce its environmental impact:
- Renewable Energy: Amazon has committed to achieving net-zero carbon emissions by 2040. The company is investing in renewable energy projects, such as wind and solar farms, to power its operations sustainably.
- Electric Vehicles: Amazon has ordered 100,000 electric delivery vans from Rivian, aiming to reduce its carbon footprint from transportation. These vehicles will be deployed in the coming years, contributing to cleaner air and reduced emissions.
- Packaging Innovations: Amazon is working to reduce packaging waste by developing more sustainable packaging solutions. The company has introduced initiatives such as Frustration-Free Packaging, which aims to minimize waste and enhance the customer experience.
Challenges and Controversies
Despite its success, Amazon has faced several challenges and controversies. Addressing these issues has been crucial for the company’s continued growth:
- Labor Practices: Amazon has faced criticism for its labor practices, particularly in its fulfillment centers. The company has been accused of demanding work conditions and low wages. In response, Amazon has implemented measures to improve working conditions, such as increasing wages and providing better benefits.
- Antitrust Concerns: Amazon’s dominant market position has raised antitrust concerns, with regulators and competitors accusing the company of unfair practices. Amazon has defended its business model, emphasizing its focus on customer satisfaction and innovation.
- Data Privacy: As a technology company, Amazon handles vast amounts of customer data. Ensuring the privacy and security of this data is a critical challenge. Amazon has implemented robust data protection measures and continues to invest in cybersecurity to safeguard customer information.
Jeff Bezos’ Professional Superpower
Jeff Bezos’s professional attributes have been instrumental in Amazon’s success. His leadership style is characterized by a focus on long-term goals, a willingness to take risks, and a commitment to continuous improvement. Bezos is known for his “Day 1” philosophy, which emphasizes the importance of maintaining a startup mindset and constantly innovating.
Bezos is also a strong advocate for data-driven decision-making. He believes in using data to inform business strategies and improve customer experiences. This approach has led to numerous innovations and improvements in Amazon’s operations.
Conclusion
Amazon’s journey from a garage bookstore to a trillion-dollar eCommerce empire is a testament to strategic planning, innovative thinking, and a relentless focus on customer satisfaction. By expanding its product offerings, investing in technological innovation, and prioritizing customer service, Amazon has built a global brand that continues to shape the future of retail. Jeff Bezos’s visionary leadership and professional attributes have been crucial in driving the company’s success. As Amazon faces new challenges and opportunities, its commitment to innovation and sustainability will be crucial in maintaining its leadership position in the ever-evolving eCommerce landscape.